- Abracon
- Adam Tech
- Aerospace, Defense & Marine
- Agastat
- AIC
- AKM Semiconductor
- Alcoswitch
- Allegro
- Alps Electric
- Altera
- AMI Semiconductor
- AMP
- ams
- Analog Devices (ADI)
- Aptina Imaging
- Atmel
- Avago / Broadcom
- AVX
- Axicom
- Bccomponents
- Beyschlag
- BI Technologies
- Bourns Inc.
- Bowei Integrated Circuits
- Bridgelux
- Buchanan
- California Micro Devices
- Catalyst Semiconductor
- CGS
- Cirrus Logic
- Citizen Electronics
- CML Microcircuits
- Coiltronics
- Cooper Bussmann
- Corcom
- Core Logic
- Cree
- CSR PLC
- CTS
- Cypress Semiconductor
- Dale
- Data Image
- Deutsch
- Diodes Incorporated
- DOMINANT Opto Technologies
- E-T-A
- Eaton
- ECS
- Edison Opto
- Elcon
- EPCOS
- Epistar
- Epson
- Everlight Electronics
- Exar
- Fairchild Semiconductor
- FCI
- Freescale Semiconductor
- Fremont Micro Devices (FMD)
- Fujitsu Semiconductor
- Fulltech Electric
- General Semiconductor
- Harvatek
- Holsworthy
- Hsuan Mao Technology
- IDT
- Infineon Technologies
- Innolux
- International Rectifier (IR)
- Intersil
- IRC
- ISSI
- IXYS-IC
- Jing Cheng Electronical
- JL World
- Johanson Dielectrics
- Johanson Technology
- JRC / NJR
- JST
- KEC
- Kilovac
- Kingbright
- Kyocera Industrial Ceramics
- LEDiL
- Linear Technology / ADI
- Lite-On Technology
- Littelfuse
- Lumex
- Lumileds
- Luminary Micro
- Luminus Devices
- Macronix
- Maojwei / ZJPT
- Maxim Integrated
- MCC
- Mean Well Enterprises
- Microchip Technology
- Micron
- Microsemi
- Mini-Circuits
- Molex
- Murata Manufacturing
- Murata Power Solutions
- MWT
- National Semiconductor
- Nichicon
- Nippon Chemi-Con
- NJR / JRC
- NVE
- NXP Semiconductors
- OEG
- Omnivision
- ON Semiconductor
- Optek Technology
- Optrex
- OSRAM Opto Semiconductors
- OTAX
- Panasonic
- Peregrine(pSemi)
- Potter & Brumfield
- Power Integrations
- PowerStor
- Preci-Dip
- Prewell
- Products Unlimited
- Pulse Electronics
- PulseCore Semiconductor
- Qorvo
- Raychem
- Renesas Electronics
- RFMD
- Richtek Technology
- ROHM Semiconductor
- Rubycon
- Samsung Electro-Mechanics
- Samsung Semiconductor
- Schaffner
- Schrack
- Seiko Instruments, Inc. (SII)
- Semtech
- Sensata
- Seoul Semiconductor
- Sfernice
- Sharp Display
- Sharp Microelectronics
- Silicon Labs
- Siliconix
- Skyworks Solutions
- SoniCrest / JL World
- Spansion
- Sprague
- Stanley Electric
- STMicroelectronics
- Sunny Electronics
- Susumu (SSM)
- Taimag
- Taiyo Yuden
- TDK
- TDK-Lambda
- TE Connectivity
- Teccor
- Texas Instruments (TI)
- Thin Film
- Tianma Micro-electronics
- TOCOS
- TOKO
- Toshiba Electronic Components
- TT Electronics
- Tusonix
- TXC
- Tyntek
- Vishay
- Vishay Precision Group
- Vitramon
- Walsin Technology
- Weidmuller
- Welwyn
- Wickmann
- Winbond
- Xilinx
- Yageo
- Zetex Semiconductors
- ZJPT / Maojwei
News
Toshiba Launches Enterprise SSDs Using 15nm MLC NAND Flash Memory
2016-02-23 | ReturnFebruary 23, 2016
TOKYO — Toshiba Corporation’s (TOKYO: 6502) Semiconductor & Storage Products Company today announced the launch of the “HK4R Series” and the “HK4E Series” of enterprise SSDs integrating NAND chips fabricated with 15nm MLC process technology. Sample shipments start from today.
The new products are Toshiba’s first enterprise SSDs integrating 15nm MLC NAND flash memory. The line-up including products with double the capacity of conventional Toshiba products[1] were developed utilizing the technology. These SSDs expand Toshiba’s enterprise storage solutions and flexibly meet various diversified requirements of the rapidly growing enterprise market.
The SSDs are equipped with Toshiba’s proprietary QSBC (Quadruple Swing-By Code) error correction technology, a highly efficient error correction code (ECC). Along with the power loss protection and data protection features, it helps strengthen the protection of customer data and enhances reliability.
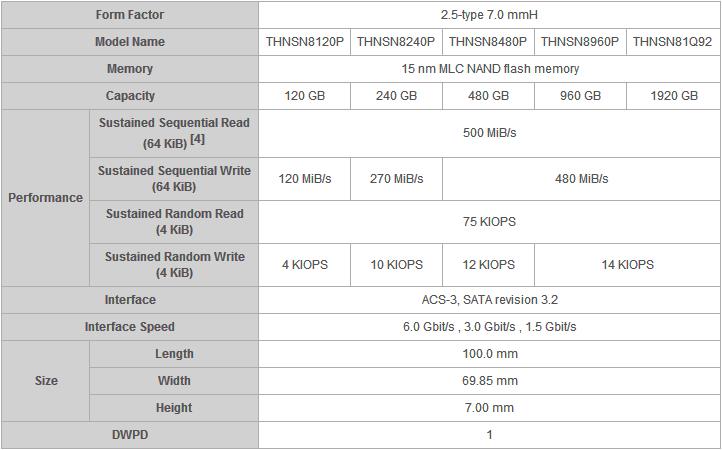
The HK4R Series is capable of one DWPD[2] endurance, and is available in capacities up to 1920GB[3], and suited for enterprise applications including web servers, files servers, media streaming, video-on-demand, search engines and warm data storage.
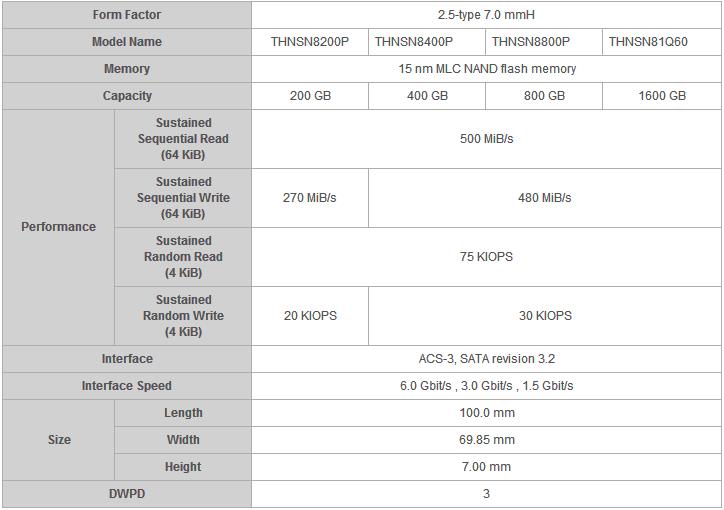
The HK4E Series of value-endurance drives offer an endurance level of three DWPD and capacities up to 1600GB. It is suited for e-mail servers and data centers.
Toshiba will continue strengthening its SSD lineup, meeting the various needs of users and leading the continuously expanding SSD market.
Outline of the New Products
“HK4E Series”
Notes:
[1] Compared with the HK3R2 series and the HK3E series.
[2] DWPD: Drive Write Per Day. One full drive write per day means the drive can be written and re-written to full capacity once a day every day for five years, the stated product warranty period. Actual results may vary due to system configuration, usage and other factors.
[3] Definition of capacity: Toshiba defines a megabyte (MB) as 1,000,000 bytes and a gigabyte (GB) as 1,000,000,000 bytes. A computer operating system, however, reports storage capacity using powers of 2 for the definition of 1GB = 230 = 1,073,741,824 bytes and therefore shows less storage capacity. Available storage capacity (including examples of various media files) will vary based on file size, formatting, settings, software and operating system, such as Microsoft Operating System and/or pre-installed software applications, or media content. Actual formatted capacity may vary.
[4] Toshiba defines a kibibyte (KiB) as 1,024 bytes (210) and a mebibyte (MiB) as 1,048,576 bytes (220).
Read and write speed may vary depending on the host device, read and write conditions, and file size.
- Follow this link for more on the new products.
“HK4R Series”
http://toshiba.semicon-storage.com/ap-en/product/storage-products/enterprise-ssd/hk4r.html
“HK4E Series”
http://toshiba.semicon-storage.com/ap-en/product/storage-products/enterprise-ssd/hk4e.html