Manufacturers
- Abracon
- Adam Tech
- Aerospace, Defense & Marine
- Agastat
- AIC
- AKM Semiconductor
- Alcoswitch
- Allegro
- Alps Electric
- Altera
- AMI Semiconductor
- AMP
- ams
- Analog Devices (ADI)
- Aptina Imaging
- Atmel
- Avago / Broadcom
- AVX
- Axicom
- Bccomponents
- Beyschlag
- BI Technologies
- Bourns Inc.
- Bowei Integrated Circuits
- Bridgelux
- Buchanan
- California Micro Devices
- Catalyst Semiconductor
- CGS
- Cirrus Logic
- Citizen Electronics
- CML Microcircuits
- Coiltronics
- Cooper Bussmann
- Corcom
- Core Logic
- Cree
- CSR PLC
- CTS
- Cypress Semiconductor
- Dale
- Data Image
- Deutsch
- Diodes Incorporated
- DOMINANT Opto Technologies
- E-T-A
- Eaton
- ECS
- Edison Opto
- Elcon
- EPCOS
- Epistar
- Epson
- Everlight Electronics
- Exar
- Fairchild Semiconductor
- FCI
- Freescale Semiconductor
- Fremont Micro Devices (FMD)
- Fujitsu Semiconductor
- Fulltech Electric
- General Semiconductor
- Harvatek
- Holsworthy
- Hsuan Mao Technology
- IDT
- Infineon Technologies
- Innolux
- International Rectifier (IR)
- Intersil
- IRC
- ISSI
- IXYS-IC
- Jing Cheng Electronical
- JL World
- Johanson Dielectrics
- Johanson Technology
- JRC / NJR
- JST
- KEC
- Kilovac
- Kingbright
- Kyocera Industrial Ceramics
- LEDiL
- Linear Technology / ADI
- Lite-On Technology
- Littelfuse
- Lumex
- Lumileds
- Luminary Micro
- Luminus Devices
- Macronix
- Maojwei / ZJPT
- Maxim Integrated
- MCC
- Mean Well Enterprises
- Microchip Technology
- Micron
- Microsemi
- Mini-Circuits
- Molex
- Murata Manufacturing
- Murata Power Solutions
- MWT
- National Semiconductor
- Nichicon
- Nippon Chemi-Con
- NJR / JRC
- NVE
- NXP Semiconductors
- OEG
- Omnivision
- ON Semiconductor
- Optek Technology
- Optrex
- OSRAM Opto Semiconductors
- OTAX
- Panasonic
- Peregrine(pSemi)
- Potter & Brumfield
- Power Integrations
- PowerStor
- Preci-Dip
- Prewell
- Products Unlimited
- Pulse Electronics
- PulseCore Semiconductor
- Qorvo
- Raychem
- Renesas Electronics
- RFMD
- Richtek Technology
- ROHM Semiconductor
- Rubycon
- Samsung Electro-Mechanics
- Samsung Semiconductor
- Schaffner
- Schrack
- Seiko Instruments, Inc. (SII)
- Semtech
- Sensata
- Seoul Semiconductor
- Sfernice
- Sharp Display
- Sharp Microelectronics
- Silicon Labs
- Siliconix
- Skyworks Solutions
- SoniCrest / JL World
- Spansion
- Sprague
- Stanley Electric
- STMicroelectronics
- Sunny Electronics
- Susumu (SSM)
- Taimag
- Taiyo Yuden
- TDK
- TDK-Lambda
- TE Connectivity
- Teccor
- Texas Instruments (TI)
- Thin Film
- Tianma Micro-electronics
- TOCOS
- TOKO
- Toshiba Electronic Components
- TT Electronics
- Tusonix
- TXC
- Tyntek
- Vishay
- Vishay Precision Group
- Vitramon
- Walsin Technology
- Weidmuller
- Welwyn
- Wickmann
- Winbond
- Xilinx
- Yageo
- Zetex Semiconductors
- ZJPT / Maojwei
News
Toshiba’s Newly Developed 2200 V SiC MOSFETs Deliver Low Power Loss that Contributes to the Simplification, Miniaturization and Weight Reduction of Inverter Systems
2023-08-10 | ReturnThree-level inverters enjoy the advantage of low switching losses because the voltage applied to switching devices in the inverters during off-state is half the line voltage. Against this, two-level inverters have fewer switching modules than three-level inverters, realizing a simpler, smaller, and lighter system. However, they require semiconductors with higher breakdown voltage, as the applied voltage is equal to the line voltage. Also, demand for semiconductors with both low loss and high breakdown voltage is growing as 1500 V DC line voltage systems are introduced in photovoltaic and other renewable energy markets.
Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corporation has developed 2200 V Schottky barrier diode (SBD)-embedded SiC MOSFETs for two-level inverters in 1500 V DC voltage systems. The impurity concentration and thickness of the drift layer has been optimized to maintain the same relationship between the on-resistance and the breakdown voltage as our existing products, and also to achieve high resistance to cosmic rays, a requirement for PV systems. It has also been confirmed that embedding SBDs clamped parasitic PN junctions between the p-base regions and the n-drift layer secure high reliability in reverse conduction.
Switching energy loss for the developed all-SiC module is far lower than for the Si module (Si IGBTs + Si fast recovery diodes) with the same 2000 V rated voltage class. Estimates of inverter power dissipation found that the developed SiC module achieves higher frequency operation twice that of a conventional Si IGBT, as well as a 37% lower loss for the two-level SiC inverter against the three-level Si inverter. The higher frequency operation enables downsizing and weight reduction of other system components, such as heat sinks and filters.
Details of the achievement were reported at the PCIM Europe 2023, the international power electronics conference held in Nuremberg, Germany, and online on May 11.
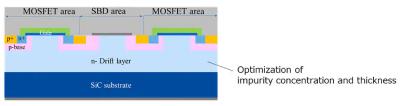
Schematic cross-sectional view of Toshiba’s 2200 V SiC MOSFET
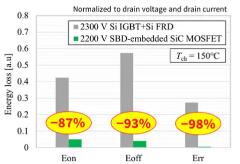
Comparison of switching energy losses between a 2300 V Si IGBT module and the all-SiC module
* Comparison of SiC module performance values (Toshiba test, March 2023) against Si module data reported prior to March 2023
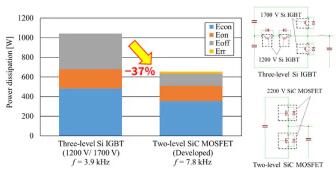
Comparison of inverter power dissipation between the conventional three-level Si IGBT and the developed two-level SiC MOSFET inverter
* Comparison of Si IGBT inverter power dissipation, based on loss characteristic data reported prior to March 2023
* Company names, product names, and service names may be trademarks of their respective companies.
* Information in this document, including product prices and specifications, content of services, and contact information, is current on the date of the announcement but is subject to change without prior notice.
Source: https://www.global.toshiba